CPP学习笔记
本文最后更新于 2025年9月23日 晚上
因课程与时间问题,无法一直使用CPP,经常需要从头拾起,故写下此篇以助快速回忆
参考书籍:
- A tour of c++
- Effective modern c++
- C++ concurrency in action
第一章 A tour of c++
1 Basic
1.1 Programs
flowchart LR
source_file1 --compile-->object_file1-->1(link)
source_file2 --compile-->object_file2-->1(link)-->exe1.2 Assignment
compare pointer and reference:
int x = 2; int y = 3;
int *p = &x; int *q = &y;
p = q // p becomes &yint x = 2; int y = 3;
int &p = x; int &q = y;
p = q // x becomes 32 Modularity
2.1 Unions
- union occupies only as much space as the largest member
- we don’t know the kind of value
union u {
int i;
float f;
};- variant need more space to store the kind of value
variant<int, char> v;
if (holds_alternative<int>(v))
get<int>(v);- enumerations
enum class Color { red, blue, green };
Color col = Color::red;2.2 Modules (C++20)
- translation unit(a source file -> a unit)
- the include is only the copy and paste
- why modules?
- the include will be handle n times in n translation units
- avoid macro affect
// vector.cpp
module;
export module Vector; // define the module called "Vector"
export class Vector { // declare
//...
}
// define
//...
// other.cpp
import Vector;
//...2.3 Exceptions
- keywords: <stdexcept>, noexcept
- we need invariant to avoid exceptions(assert/static_assert)
- chatgpt will do the things
2.4 Function Arguments
- pass by value / pass by reference(const &r)
- default function argument
- overloading
- return with move
TYPE f() {
TYPE i;
return i;
}- structured binding
struct Entry {
string name;
int value;
}
Entry read_entry(istream &is) {
string s;
int i;
is >> s >> i;
return {s, i};
}
auto [n, v] = read_entry(cin); // unpackthe types are deduced from return type
map<string, int> m;
for (const auto &[k, v] : m) {
//...
}3 Classes
- always use explicit constructor
- define a class
class complex {
double re, im; // representation: two doubles
public:
complex(double r, double i): re{r}, im{i} {}
complex(double r): re{r}, im{0} {}
complex(): re{0}, im{0} {}
double real() const { return re; }
void real(double d) { re=d; }
double imag() const { return im; }
void imag(double d) { im=d; }
complex& operator+=(complex z)
{
re+=z.re;
im+=z.im;
return ∗this;
}
complex& operator−=(complex z)
{
re−=z.re;
im−=z.im;
return ∗this;
}
};- using initializer_list
// the {1, 2, 3} was converted to initializer_list
Vector(std::initializer_list<double>);
//...
Vector v1 = {1, 2, 3};- abstract types
class Container {
public:
virtual double& operator[](int)=0;
virtual int size() const = 0;
}
class VectorContainer: public Container {
//...
}- virtual function table(vtbl)
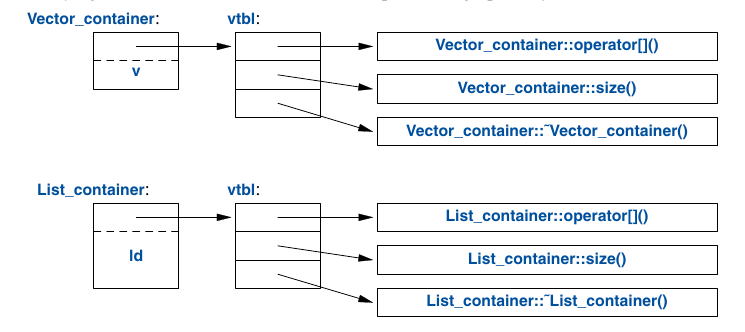
- using dynamic_cast to find hierarchy
// Shape -> Smiley, the obj is Shape
if (Smiley* p = dynamic_cast<Smiley*>(obj)) {
// ...
}- resource acquisition is initialization(RAII)
4 Templates
- example
template<typename T>
class Vector {};- function object
template<typename T>
class LessThan {
//...
bool oprerator()(const T& x) const return { x < val; }
}- lambda expression
- type trait
- aliases(
using) if constexpr
5 Concepts
- define
template<typename T>
concept Incrementable = requires(T a) {
{ ++a } -> std::same_as<T&>;
};- using
template<Incrementable T>
void incrementAndPrint(T value) {
++value;
std::cout << "Value after increment: " << value << std::endl;
}
int num = 1;
incrementAndPrint(num)template <typename T, typename S,
typename = std::enable_if_t<std::is_base_of_v<Target, T> &&
std::is_base_of_v<Search, S>>>- fold expression
template<Number... T>
int sum(T... v) {
return (v + ... + 0); // right fold: (v[0] + (v[1] + (v[2] + 0)))
}
int x = sum(1, 2, 3);
int y = sum('a', 2.4);- perfect forwarding
6 library
-
std::swap(a, b)
-
hash
-
string/string streams
-
regular expression
-
iterators
-
io
-
file system/file streams
-
containers: vector/list/map/set
- map --> rb_tree
- unordered map --> hash table
-
head files
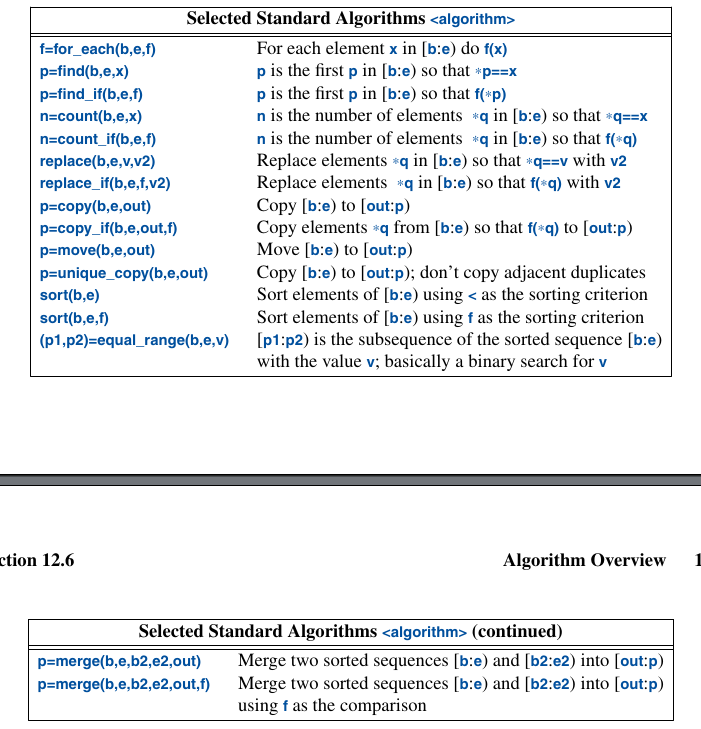
- algorithm
- unique_ptr/shared_ptr/weak_ptr
- move/forward
- bitset/pair/tuple
- variant/optional/any
- span/mem_fn/enable_if
第二章 Effective modern c++
类型推导
第三章 C++ concurrency in action
基础
-
并发/并行,线程/进程
-
阿姆达尔定律
-
thread/join/detach/call_once/once_flag
-
竞争条件/临界区/mutex/细粒度/互斥
-
经典IPC问题,参考:操作系统设计与实现
第四章 零零碎碎
-
移动构造函数/赋值函数/析构函数建议添加noexcpt,因为像vector这种容器是强类型安全的,加上noexcpt可以优化拷贝行为
-
emplace_back优于push_back,可以直接传参构造,避免拷贝开销
-
https://www.cnblogs.com/neooelric/p/10878394.html
- run of five -> copy and swap -> move
- collapsed
- 函数返回的优化(移动)是编译器层面的优化
- 移动只能为资源管理带来优化
if(类内没有掌管任何资源) {
五个特殊成员函数一个都不用实现, 编译器自动提供的默认实现就完全够用
并且你能从其提供的默认移动构造函数与默认移动赋值操作符中获得性能提升
} else if(类掌管了资源){
if (拷贝资源的开销 > 移动资源的开销) {
五个特殊成员函数都实现一遍, 当然具体实践的时候可以采用 rule of four and a half的方式, 不实现移动赋值操作符
} else {
仅实现三个古典的特殊成员函数. 不需要实现移动构造函数和移动赋值操作符
}
}CPP学习笔记
https://gentlecold.top/20240212/cpp-note/