CMU15445-Fall2023课程笔记
本文最后更新于 2025年7月2日 晚上
课程笔记
Overview
- algebra
- vector database for ai
- relational languages
- dml/ddl/dcl
SQL
- aggregates/group by/having
- string operations/date operations/output redirection
- window functions(over/partition by)
- nested queries
- lateral join
- common table expressions(with as)
- union/intersect/except
Database storage
- outline
flowchart LR
DiskManager-->BufferPoolManager-->AccessMethods-->OperatorExecution-->QueryPlanning- volatile(bytes addressable) / non-volatile(block)
- sequential / random access
- why not use os(mmap, Virtual memory)?
Three storage approaches
- heap file --metadata track–> page(with header) -> tuple
- tuple oriented storage
- slotted pages/record ids
- denormalized(pre-join) tuple data
- log structured storage(good for write-heavy workloads)
- coalesce
- sorted string tables
- index organized Storage
- can be sorted and using binary search
Inside tuple
- word-aligned tuples
- variable precision numbers/fixed precision numbers
- null data types(bitmap/special value)
- large data
Storage models / Compression
- oltp/olap/hybrid(htap)
- row is for oltp/col is for olap
three storage models
- n-ary storage model/decomposition storage model/hybrid storage model(pax)
- DSM: how to merge a complete tuple(dictionary compression)
- partition attributes across(pax)
database compression
- block level
- general-purpose algorithm(zstd)
- tuple-level
- attribute-level
- column-level
- run-length encoding
- bit packing
- bitmap encoding
- delta encoding
- dictionary compression
Database memory
- locks/latches
- buffer pool optimization
- multiple buffer pools
- pre fetching
- scan sharing
- buffer pool bypass
- lru/lru-k/mysql approximate lru-k
- fsync errors(there is a page cache between file disk and file system), so use direct IO
Hash tables
- hash function/hash collision
hash function
- facebook xxhash3/google farmhash
static hashing schemes
- probe hashing/cuckoo hashing
dynamic hashing schemes
- chained hashing
- bloom filters(false positives sometimes occur, tell you a key is exists maybe wrong)
- extendible hashing
- linear hashing
B+ tree
- B+Tree has a better concurrency access than B tree
- selection conditions/duplicate keys
- clusted b+ tree
design choices
- node size
- merge threshold
- variable length keys
- intra node search
optimization
- prefix compression/suffix truncation
- deduplication
- pointer swizzling
- bulk insert
- write optimized b+ tree(delay update)
Index concurrency control
- test and set spinlock(atomic)/blocking os mutex(mutex)/reader writer locks(shared_mutex)
hash table latching
- page latches/slot latches
b+tree latching
Sorting / Aggregations
- in-memory sorting(quick sort)
- top-n heap sort/external merge sort(use three buffer pool page)
- general external merge sort
- double buffering(overlap cpu/io operations)
- using b+tree(cluster/uncluster) for sorting
- hashing for aggregations
Join algorithm
- early/late materialization(record id)
- (block/index)nested loop join/sort merge join/hash join
- use smaller table as outer table
- partitioned hash join
- hybrid hash join
Query Execution
processing model
- iterator model
- materialization model
- vectorization model
- plan processing direction
access methods
- sequential scan
- zone maps
- index scan
- multi-index scan
- modification query
- Halloween problem
expression evaluation
-
JIT compile
-
scheduler
-
parallel/distribute database
-
process/thread/ per worker
-
sql server
-
embedded dbms
-
intra query parallelism
-
intra-operator parallelism(horizontal)
- gather/distribute/repartition
-
inter-operator parallelism(vertical)
-
bushy parallelism
-
io parallelism(RAID)
Query planning/Optimization
- predicate pushdown
- replace Cartesian product
- projection pushdown
- hyperloglog
Concurrency control
- ACID
- ensuring atomicity: logging/shadow paging
- ensuring isolation: pessimistic/optimistic
- dependency graph
- conflict serializable/view serializable
2Phase locking
- shared/exclusive lock
- strong 2pl(avoid cascading abort)
- deadlock detection/prevention
- waits-for graph
- deadlock handling: find victim/completely roll back/partial
- deadlock prevention: wait-die/wound-wait(using priority)
- lock granularity/hierarchy
- intention locks: is/ix/six
Timestamp ordering concurrency control
- can’t read from the future(rw)
- can’t write if future has read/write(wr, ww)
- thomas write rule
- optimistic concurrency control
- read Phase
- validation Phase(three cases)
- write Phase(serial commits/parallel commits)
- phantom problem(insert/delete)
- re-execute scans
- predicate locking
- index locking
- isolation level
- serializable
- repeatable read(phantom read)
- read committed(non-repeatable read/phantom read)
- read uncommitted(dirty read/non-repeatable read/phantom read)
Multi-version concurrency control
- read/write do not block each other
- when write, create a version/when read, read the newest version
- snapshot isolation(write skew anomaly)
mvcc design decisions
- concurrency control protocol: timestamp/occ/2pl
- version storage:
- append-only(old-new chain/new-old chain)
- time-travel
- delta
- garbage collection:
- tuple level
- transaction level
- index management
- secondary indexes
- logical pointers/physical pointers
- duplicate key
- deletes
- deleted flag
- tombstone tuple
Logging
- system failures: software / hardware
- steal policy/force policy
- shadow paging
- write-ahead log: steal + no force
- logging schemes: physical/logical/physiological
- checkpoints
Recovery
- algorithm for recovery and isolation exploiting semantics(ARIES)
- steal/no force
- log sequence number
- log - LSNs
- disk - pageLSNs
- dram- flushedLSNs
- for redo: compensation log records
- for checkpoints: active transaction table/ dirty page table
- fuzzy checkpoints
- ARIES
-
- analysis
-
- redo
-
- undo
-
Distributed databases
- parallel vs distributed
- shared nothing
- shared disk
- homogenous node/heterogenous node
- vertical partition/horizontal partition
- consistent hashing
- transaction coordination
- centralized/decentralized
- distributed concurrency control
Distributed OLTP
- replication
- primary-replica/multi-primary
- k-safety
- propagation scheme
- synchronous
- asynchronous
- atomic commit protocol
- paxos
- CAP / PACELC
- google spanner
Distributed OLAP
- star schema
- snowflake schema
- push query to data/pull data to query
- query fault tolerance
- cloud systems
- data lakes
Vector database
- vector index
- inverted file
- hierarchical navigable small world
项目思路
项目准备
- 判分:
gradescope: KK5DVJ
- 讨论:
- 使用clang:
set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER "/usr/bin/clang")
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER "/usr/bin/clang++")这玩意儿放的位置很迷
P0. C++ Primer
Think basic
- what is a trie? https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28891541
- what is copy on write? 即修改的时候再复制而不是直接复制:https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-cn/寫入時複製
- why copy on write? 每次修改都会产生一个新的trie,如果不能影响到原来的trie,需要尽量复用节点
- 智能指针可通过get获取原始指针,可用dynamic_cast判断派生类指针
Task1
- Get: 找到后用dynamic_cast把指针改成指向TrieNodeWithValue
- Put: 所有经过的节点都需要克隆
- 因为Put是一个const函数,所以不能修改root!
- 所有sharedptr都是const TrieNode,只有uniqueptr是non-const的,That’s why the return of Clone is unique!
- 所以本质就是non-const unique->const shared,因为shared是const
- why use unique? 如果是non-const shared,把它改了那所有的引用都改了
- 还要注意空字符串/root_初始为nullptr!
- **map的insert方法不会自动替换相同的键的值!**要么用[]要么用insert_or_assign!!
Task2
- 这时候就可以看到COW的好处了:读写共存(如果不考虑一致性)
Task3
- 本来使用lldb调试的,不知道为什么无法显示继承类的定义,遂改成gdb调试
Task4
- 利用transform实现大小写转换:
std::transform(val.begin(), val.end(), std::back_inserter(result), ::tolower);Result

P1. Buffer Pool
Task1
- LRU-k
- 比较第前k次的访问时间
- 如果访问次数未超过k次,则认为时间为+inf
- 如果有多个+inf,则按照LRU的方式比较(比较最早的那次访问)
- 相当于访问次数未超过k次的不计入缓存
- 这样即考虑了访问频次又考虑了访问时间
Task2
- 实现DiskScheduler,创建后台线程负责处理所有的IO请求
Task3
- 结合替换算法/IO处理,实现缓存管理器,整理逻辑如下:
flowchart
subgraph important
a[page_id on disk] --> b[frame_id on buffer]
end
LRUKReplacer --> BufferPoolManager
DiskScheduler --> BufferPoolManager
BufferPoolManager --> NewPage --> c[new and pin the page]
BufferPoolManager --> FetchPage --> g[pin the page, get page to disk]
BufferPoolManager --> UnpinPage --> d[unpin the page]
BufferPoolManager --> FlushPage --> e[write page to disk -f]
BufferPoolManager --> DeletePage --> f[delete page from disk]- 注意多线程,两个fetch同一个frame的情况,pincount相当于引用计数
- unpinpage时如果找到页就将其设为是否可替换(注意isdirty的true->false这种情况不存在,如果原来是脏页不能直接变成false)
- page的读写锁不是必需的(不会在pin住page的情况下修改page中内容),在一把大锁保平安的基础上
- 别把必要的函数放到assert里面!!!
优化
- 如果是顺序扫描,则尽量不替换顺序的page(后一个page会被访问,前一个page不会被访问,从而可以调整替换策略)
- 并行化IO,需要保证IO操作的顺序,未实现
- 如果只锁一个mutex,优先用 unique lock 相对于 scoped lock
Result

P2. Hash Table
其实可以直接奔着task3去做,很多辅助函数暂时用不到,或者等重构的时候再实现,此project的目标就是实现find/insert/delete三个接口
另外由于许多类都提前定义好了,需要额外关注下成员变量(比如page_guard别忘了dirty变量)
要求实现的是Extendible Hash,主要难点在于插入和删除
此数据结构的一些特点:
- 添加了一个header,通过most-significant bit来索引directory,而通过least-significant bit来索引bucket,添加header是为了提供更好的并发能力
- directory size 必定是2的幂次方
- local depth 的作用是指示directory中有几个指向了bucket:
- local depth <= global depth
- 虽说是可扩容的,但仍无法超过最大限制,比如directory的max depth为4,如果第一个bucket满了,那么无法再插入最后4位为0000的数了
Insert的几种Case(方括号表示local depth):
- 正常Insert,返回
- bucket已满,需要扩容,Local depth必定增加:
- 初始情况这4个bucket_idx都指向同一个bucket,在110的位置插入并且overflow
- 找到另一类新bucket的位置
- 另一类bucket:比如depth为1时,所有的0都指向同一个bucket,当depth增长为2时,多出来的一位就可以进行区分(10/00)
- 更新那一路的bucket(可能有多个)
- 更新local depth/remap directory,重新分发bucket中的元素
- 找到另一类新bucket的位置
00[0] -> 0[00] <-- new bucket idx
01[0] -> 0[10]
10[0] -> 1[00]
11[0] -> 1[10] <-- current bucket idx- 需要增加global depth:
- 复制前一半的元数据
- 再进行bucket的remap和redistribute
[00] -> [000] <- current bucket idx
0[1] -> 00[1]
[10] -> 0[10]
1[1] -> 01[1]
-> [100] <- new bucket idx
-> 10[1]
-> 1[10]
-> 11[1]注意重新分配后仍有可能无法插入,此时需要继续扩容(循环进行直到无法扩容或插入成功)
Remove的case:
- 考虑删除后的shrink
- 不同于Insert,shrink
只考虑global depth = local depth的情况(不能加这个限制条件,否则可能都是空桶但仍然无法shrink) - why shrink: 当10指向的bucket为空时,就可以释放这个bucket并将此处索引映射到00的bucket,有两个位置指向同一个bucket,因此减小local depth
- 当且仅当所有local depth小于global depth时,才会进行shrink
- 不同于Insert,shrink减小global depth,不用再进行额外的元数据操作
- 存在多次shrink的情况,比如下图,如果01位置的bucket为空,当00的bucket为空并进行shrink后,此时需要继续shrink(another bucket is empty)
[00] -> 0[0] <-- bucket idx
0[1] -> 0[1] <-- another bucket
[10] -> 1[0]
1[1] -> 1[1]Task1
- 用pageguard封装page,负责其latch/pincount的释放
- 细分为writepageguard和readpageguard,分别对应写锁和读锁
- 注意unpinpage传入的dirty是guard自身的dirty成员数据
- 对于移动操作,需要先释放自己的page
- 不要忘记自身携带的dirty成员变量
Task2
- 实现各种Page的定义
- 使用INVALID_PAGE_ID来标记页的不存在
- 定义bucket的remove时,注意如果remove的是最后一个元素则直接减size即可
- cpp的类中成员变量默认值是随机的,不要忘记初始化
Task3
- 实现完整的ExtendibleHash,前两task的实现就是为此服务的
- 注意到三种Page的实现中都删除了构造函数,因为使用reinterpret_cast转换指针后无法调用构造函数
- 进行位操作时注意类型保持uint32,同时注意无符号类型倒序遍历时当i=0后再减一会溢出
- uint32 类型的数据右移32位会导致数据没有变化?(如果移动位数超过类型位数,会自动取余)
锁优化
-
得益于pageguard的实现,我们可以轻松进行锁优化
- GetValue:
flowchart LR a[rlock header] --> b[rlock directory] --> c[unlock header] --> d[rlock bucket] --> e[unlock directory] --> f[get value]- Insert:
flowchart LR a[wlock header] --> b[wlock directory] --> c[unlock header] --> d[wlock bucket] --> g[insert value]- Remove:
flowchart LR a[rlock header] --> b[wlock directory] --> c[unlock header] --> d[wlock bucket] --> g[remove value] -
注意到header仅在insert时会进行修改(remove的shrink没有要求删掉directory),可以用bitmap记录是否有directory(锁仍是必需的,因为要保证bitmap操作的线程安全)因为仍要锁,实际并无增益 -
在判断插入无需grow或者删除shrink时,即可释放directory锁
-
刚开始对directory用读锁,如果发现directory需要修改,则用写锁重头来过(经过测试只对remove操作这样做,因为shrink发生的情况较少)
Result
以上优化只是个人思路,实际实操并没有明显提升(qwq)
最终结果:

P3. Query Execution
有几个概念还是很抽象的:
- plan node,查询节点,包含expression用以构造tuple
- schema,生成tuple的列名
- executor,算子,通过next返回处理过的tuple
- catalog,存储数据库的元数据
- expression,通过evaluate返回Value
查询逻辑为:
- Parser,将sql语句解析为语法树
- Binder,根据语法树绑定为数据结构,这样才可以通过编程语言的方式进行控制
- Planner,生成查询节点(通过explain查看得到的
- Optimizer,根据规则优化查询节点
- Executor,执行查询
整个执行过程是iterator的(pull-based的火山模型)
优化器是从children开始优化的
实验中许多情况默认内存可以放下数据,这样代码更好写,否则就要考虑partitioned hash了
Task1
- 优化器会将filter执行器优化至seqscan中
- 源代码已解决Halloween problem:
// When creating table iterator, we will record the maximum RID that we should scan.
// Otherwise we will have dead loops when updating while scanning. (In project 4, update should be implemented as
// deletion + insertion.)
RID stop_at_rid_;- 通过列名比较索引的列和filter的列是否相等(索引的列名还要拼接表名)
- 因为只要求对
where v = 1的情况优化为index scan,所以只用比较一个列
Task2
- Aggregate key 对应的是 group by 得到的列值
- Aggregate value 对应的是通过expr得到的value(例如sum()得到的就是tuple那一列的值,count()得到的就是1)
- 两者通过std哈希表映射(不考虑内存放不下的情况)
- count* 与 count(col) 的区别在与后者只统计非空值
Task3
- 哈希表的value记录多个Tuple values/RID(late materialization)
- 如果是left join,把右表作为outer table
- 优化器实现中,使用递归处理相对更易编写
Task4
- 使用优先队列进行topk优化(比如要获得k个最大值,则创建最小堆,复杂度为nlogk)
- window function中注意rank,如果两个tuple根据order by的值相等,则rank不增加;如果没有order by,则都是1
优化
// TODO
P4. Concurrency Control
- 实验要求的是MVOCC,乐观锁,即后处理冲突
- 除bonus task外,要求的隔离级别为snapshot-isolation,此隔离级别需要解决dirty read/non-repeatable read问题
- 实验通过记录时间戳的方式解决以上问题
Task1
这一部分负责安排分配时间戳
- watermark返回所有运行中txn的最小read_ts,通过map记录所有的read_ts,可以在commit/abort txn后快速找到下一个最小的read_ts
- begin txn 不需要增加ts,commit需要,因为同一时刻只能有一个txn commit,而begin没有限制
Task2
这一部分安排seq scan的事务操作(相当于读操作)
-
tableheap中(即磁盘上)是最新的记录,而undo日志记录ts时刻的tuple记录(增量记录)
-
reconstruct 的作用即把最新的tuple回退到以前的tuple
-
检查重构的tuple是否处于删除状态
-
需要重新修改commit操作,将table heap中的ts更新 -
注意read_ts为0时对应的undo log
-
只有两种情况需要回退:
// 1. the newest is not commited and the cur txn is not the newest's txn(not commited, not visible) // 2. commited. but can't read from future
Task3
- 写冲突:
- 最新版本已经commit,但写操作发生在一个之前的版本
- 最新版本未commit,当前事务并非此事务
- 若发生写冲突,则设置为tainted并抛出异常
- 可以使用UpdateTupleInplace,因为此部分规定类型尺寸是固定的
- 注意undo log是增量记录,如果将1改为2又改回1,依然认为此列被修改
- catalog 有个 gettablenames 的接口来获得所有table
Task4
- 删除tuple并不会删除主键,所以版本链中存在tuple删了又有的情况
- 为什么不删主键呢,因为index scan需要主键查找到以前的版本
- 更新时如果主键也被更新,先将所有涉及到的tuple mark为delete再进行更新
- 由于hash index只支持点查询,所以很多情况不用考虑(Halloween problem)
- 如果是在主键上进行update,先delete所有,再update
- 如果将主键列的值全改为一个相同的值,此时需要抛出异常
- 并发中,存在多个事务同时update同一个tuple的情况(并发下,不能仅仅通过ts_考虑冲突,如果不加锁,肯定存在绕过if的情况)
- 主要冲突在于版本链(所有的读取都是依赖于Heap上的值/undo log)
- 务必在更新heap之前,先处理好版本链的更新,在版本链的更新中处理好冲突
- 更新版本链无外乎两种情况:append新的log,modify之前的log
- 注意这里的冲突讨论的都是逻辑冲突,和操作相关的内存冲突已经通过latch避免
UpdateUndoLink->UpdateVersionLink,GetUndoLink->GetVersionLink- 利用check和in_progress进行保护,在commit时修改inprogress(同时注意修改应该保持原子性
- 如果发生写冲突,
但是如果正在处理的事务commit后的ts仍小于另一个事务的readts这种情况不可能发生,此时不应直接abort - UpdateVersionLink成功后需要再次检查写写冲突(如果有个事务提交了)
Bonus
// TODO
Result
实现abort的最简单逻辑后就可以减少bench1test的很多冲突,从结果来看实现bonus(通过bench2test)的人数并不多
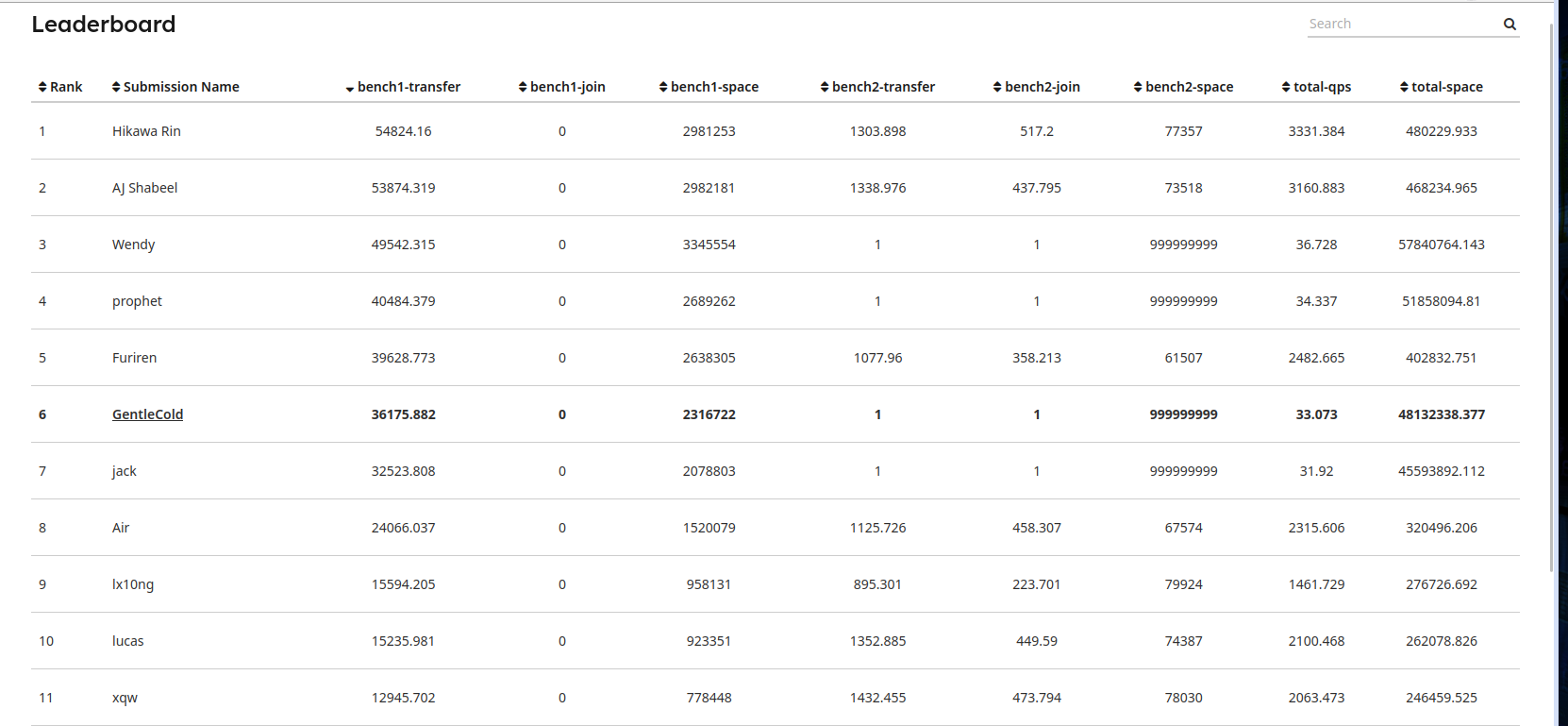
All result
不算bonus勉强通关吧、
也算是第一次从头到尾刷完国外CS的课,相见恨晚
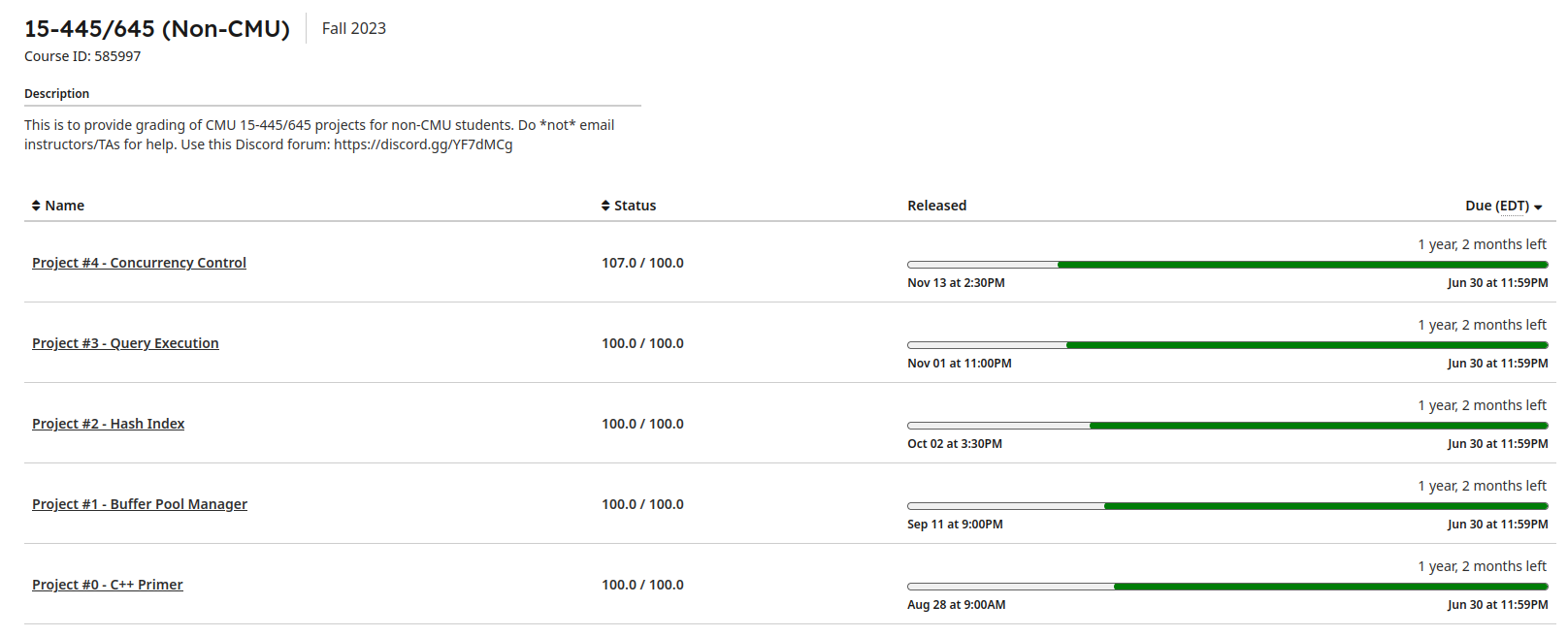
花费时间在一个月左右,外加本校课程作业压力
虽然有很多时间花费在一些很搞笑的bug上…